Use the Knowledge Base
All biGENIUS-X documentation is available in this Knowledge Base.
This article will provide tips and tricks to use it efficiently.
Public and private content
The biGENIUS-X Knowledge Base contains articles with different access levels:
- Public access: everyone can read the article content. All user manual articles for the biGENIUS-X application are public.
- Private access: only authorized users (Partners...) with a username and a password can access the article content. This is true for the partner section.
If you think you should have access to the entire Knowledge Base and don't have it yet, please ask our Support team at support@bigenius-x.com.
Table of content
The Knowledge Base articles are organized into Categories and Subcategories.
On the home page, you can click on a Category card:

The available categories are:
- Getting started: New to biGENIUS? Start exploring!
- General overview: Understand how biGENIUS as a service works
- Application Modules: How-to documentation .... for the modules of the application
- Generators: Documentation for all generators
- Discovery application: How to use our discovery application
- Best practices: Follow our best practices when starting a new project
- FAQs: For assistance with any issues you may encounter in the application, please refer to the relevant articles below
- Product Release Notes: Detailed information about each product release's changes, improvements, and bug fixes (SaaS Application, Discovery Application, and Generators).
- Legal Documents: Use our products or services? You'll want to give these a read.
This opens the following:
- The list of articles in the Category
- A dynamic table of contents where you can select another Category or Subcategory to display the list of corresponding articles
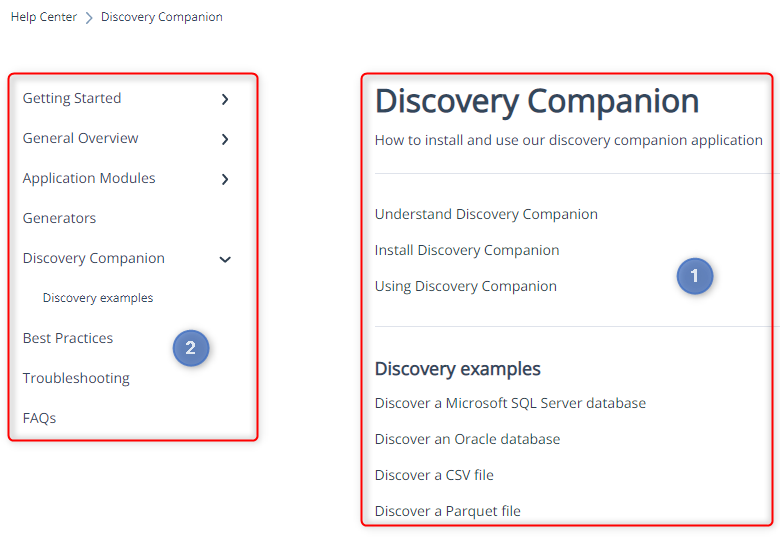
Standard layout of the articles
In the biGENIUS-X Knowledge Base, each article follows the same layout:
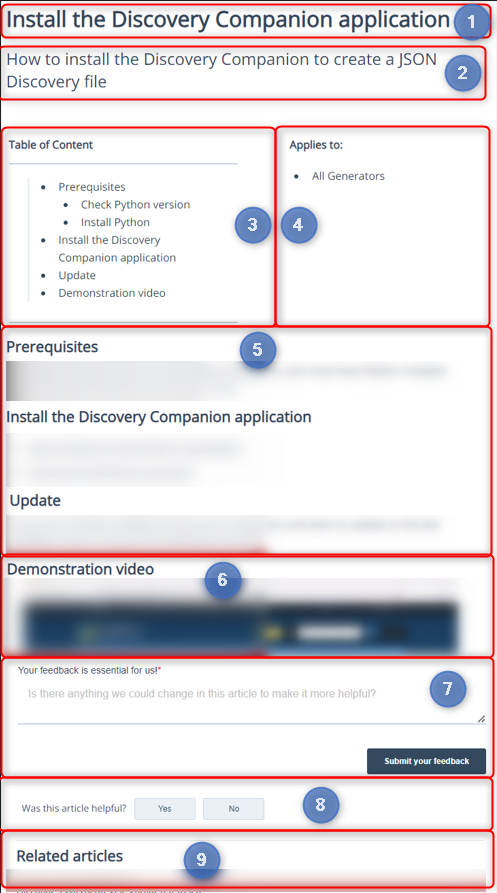 |
|
Search
The Knowledge Base provides a Search Bar:

In this Search Bar, you can use search Keywords as follows:
- Search terms are case-insensitive. For example, "user" and "User" return the same results.
-
A single-word search term returns a result if it appears in the data as follows:
- a single word
- a single word in a longer phrase
- the prefix of a longer word
-
The search term will not return a result if it appears in the data as follows:
- in the middle of a word
- at the end of a word
- When using multiple search terms, the matching logic is "OR." This means that at least one of the words should appear in the record for it to be considered a match, regardless of their order. Results with all search terms in the exact order entered will appear first.
- It is not possible to exclude keywords from the search.